Which Cells in the Small Intestine's Mucosa Secrete Mucus
The intestinal goblet cells not only secrete the MUC2 mucin but also a number of typical mucus components. B carry products of digestion that will not pass through the walls of blood capillaries.
Small Intestine Structure Function Digestive System Anatomy And Physiology
I Bio 102 Lab 03.
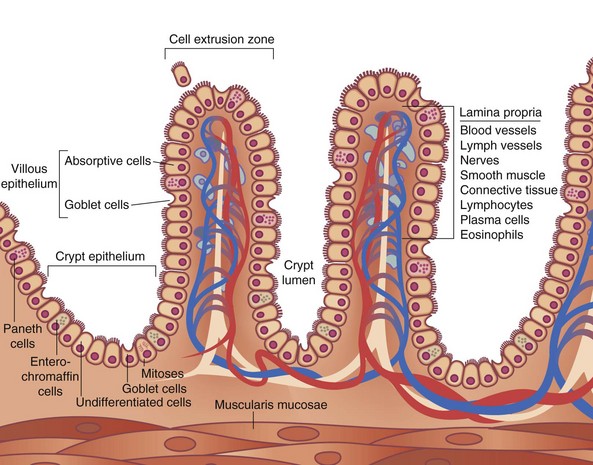
. Enterocytes have their apical surface covered by transmembrane mucins and goblet cells produce the secreted gel-forming mucins that form mucus. People also ask what cell in the mucosa of the small intestine produces mucus. The correct answer is option 2 ie.
Epithelial cells of the mucosa have embedded digestive enzymes on their tiny hair-like ____. 64 The mucosal stroma invariably becomes chronically inflamed and contains numerous macrophages and lymphocytes. 2 C arrow new mucus is secreted and after 40 min it almost reaches the same thickness as before removal.
2B in contrast to colonic explants. Intestinal epithelial cell surface is covered by two mucus layers inner firmly adherent layer and outer loosely adherent layer consisting largely of MUC2 mucin network produced by the goblet cells and other host defense molecules produced by goblet cells Paneth cells and absorptive enterocytes. It is a layer that forms the surface of both small and large intestine of the gastrointestinal tract.
How does histamine stimulate HCl secretion. The small intestinal mucosa of the pouch becomes flattened after 2 years but the epithelial cells remain columnar. 4 The absence of or any.
Microbes are associated with the outer loosely adherent. These cells provide most of the around 30 proteins that make up the core mucus proteome 2. These enzymes are peptides sucrase maltase lactase enterokinase.
Intestinal mucosal Epithelium is a part of the intestinal mucosa layer. Chemical Digestion and Nutrition. Small intestinal explants do not spontaneously secrete mucus when mounted in the chamber Fig.
This mucus along with bicarbonates from the pancreas protects the intestinal mucosa from acid as well as provide an alkaline medium for enzymatic activities. Exocrine cells in the mucosa of the small intestine secrete mucus peptidase sucrase maltase lactase lipase and enterokinase. Some of the intestinal epithelial cells called goblet cells contain small globules of mucus.
Intestinal glands at the bases of the villi secrete large amounts of watery fluid that carry digestive products into the villi. Endocrine cells secrete cholecystokinin and secretin. In crypts the epithelium also includes Paneth cells and stem cells.
Which cells in the Small Intestines mucosa secrete mucus. The parietal cells secrete acid and the resulting drop in pH causes the antral D cells to release somatostatin which inhibits gastrin release negative feedback control. The epithelial tissue layer of the small intestine contains absorptive cells which take in nutrients and goblet cells which secrete mucus.
Cells that secrete mucus in the small intestine include goblet cells which are abundant throughout the mucosa and mucus-secreting glands located in the submucosa of the duodenum. Some of the intestinal epithelial cells called goblet cells contain small globules of mucus. Which cells in the small intestines mucosa secrete mucus.
Intestinal mucus is produced by goblet cells and forms a highly organized glycoprotein network mainly consisting of mucin 2 MUC2 but also containing a stable core proteome 2. The epithelial surface forms many small projections called villi one of which occupies most of this image. This is composed of a single layer of cells.
Endocrine cells secrete cholecystokinin and secretin. Cells that secrete mucus in the small intestine include ___ which are abundant throughout the mucosa and mucus-secreting glands located in the _____ of the duodenum. C produce new cells for the mucosa of the small intestine.
Paneth cells enteroendocrine cells absorptive cells goblet cells. D secrete digestive enzymes. Mucus is formed by and secreted from specialized cells called goblet cells at surfaces or similar cell types in specialized glands.
3 4 The mucins are highly hydrophilic and can bind water to form a gel-like structure preventing direct contact between enterocytes and the intraluminal content especially pathogenic microorganisms. However upon stimulation with carbachol and PGE 2 Fig. The cell turnover rate of the intestinal epithelium exceeds that of the bladder resulting in abundant exfoliation of intestinal-type epithelial cells.
Exocrine cells in the mucosa of the small intestine secrete mucus peptidase sucrase maltase lactase lipase and enterokinase. Which cells in the small intestines mucosa secrete mucus. The purpose of mucous neck cells is to secrete mucus.
The _____ Circulation drains all of the organs of the digestive system. Mucus in the small intestine is secreted by the goblet cells present in the intestinal mucosal epithelium. CLCA1 FCGBP AGR2 ZG16 and TFF3.
Enteroendocrine cells enterocytes Paneth cells goblet cells. The small intestine has a single unattached mucus layer. Small intestinal mucosa is lined by a simple columnar epithelium which consists primarily of absorptive cells enterocytes with scattered goblet cells and occasional enteroendocrine cells.
In a patient suffering from a gastric ulcer caused by helicobacter pylori the cells most likely to have been damaged first are the _____. Goblet cell secretes mucus in intestinal mucosal Epithelium. Oxyntic cells also known as parietal cells are a type of cell of the gastric glands of the stomach.
The most important factor for regulating secretions in the. In cystic fibrosis this layer becomes attached accounting for the intestinal manifestations of this disease. Goblet cells secrete mucins which are high-molecular-weight glycoproteins denoting the primary structural element of the mucus layer.
The goblet cells have recently been shown to have a novel gate-keeping role for the presentation of oral antigens to the immune system. The most important factor for regulating secretions in the. Histamine stimulates the parietal cells via their H2 receptors.
A increase the surface area of the mucosa of the small intestine. Why are there cells in the small intestine that produce mucus.
A Small Intestine Mucosal Immune System Landscape The Intestinal Download Scientific Diagram

No comments for "Which Cells in the Small Intestine's Mucosa Secrete Mucus"
Post a Comment